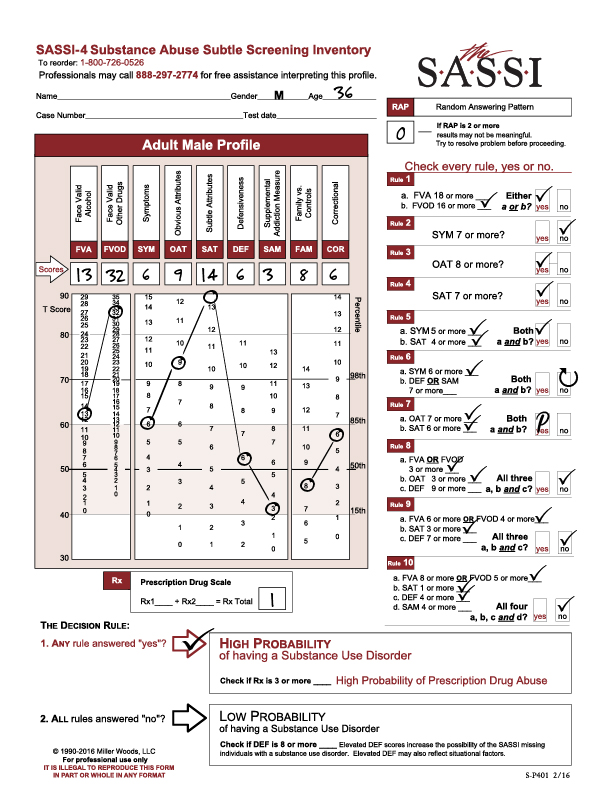
The following profile result is of a 35-year-old male referred for screening and possible assessment after a drug-related arrest. He completed the FVA/FVOD side of the questionnaire based on his entire life timeframe. His RAP score was 0, indicating no random responding and that the result should be valid. His Prescription Drug Scale score (Rx) was 1, so he did not meet the cutoff for High Probability of Prescription Drug Abuse.
Looking at this profile, we see that he was classified as high probability of a substance use disorder based on the following Decision Rules:
- Decision Rule 1 with a FVOD score of 32.
- Decision Rule 3 with an OAT score of 9.
- Decision Rule 4 with a SAT score of 14.
- Decision Rule 5 with a SYM score of 6 (5 or more) and a SAT score of 14 (4 or more).
- Decision Rule 7 with an OAT score of 9 (7 or more) and a SAT score of 14 (6 or more).
Looking at the graph on the SASSI Adult Male Profile sheet, we see an extremely high elevation on the FVOD scale score which is significantly above the 98th percentile. Individuals who score this high on the FVOD are able to acknowledge currently having or having had numerous negative consequences and problems as a result of their use of drugs. This can include loss of control of the drug use as well as using a coping mechanism. It is important to note that, since he was asked to use the “entire life” timeframe for the FVA and FVOD scales, his admission of having these consequences and problems with drugs may be related to some time in his past and not necessarily currently. For example, the client’s score on the SYM scale (which is similar to the FVA/FVOD in what it is measuring), is not nearly as elevated as his score on the FVOD even though the questions are not that dissimilar from the FVOD questions.
This suggests that he is not showing as much acknowledgement on the SYM scale of the symptoms of substance misuse that he admitted to on the FVOD scale. This could be related to the fact that the SYM scale (like all scales on the True/False side of the questionnaire) has no specific timeframe associated with it and therefore the client may have the belief that, while he has had significant problems with drugs in the past, he may not believe his current drug use is as much of a problem currently. It is highly recommended that clinicians do a content analysis of the client’s answers to the FVOD and SYM scale questions as this will provide more insight into the client’s acknowledged problems with drugs.
This client’s elevated OAT scale score, like the elevated FVOD scale score, suggests a capacity to acknowledge and identify with many of the typical negative attributes (general personality and behavioral characteristics) and personal limitations that are often common among those with substance use disorders – e.g. impatience, resentment, self-pity, impulsiveness). While the client can often see these “character defects”, they may not always feel motivated to change them or feel capable of changing. Given that the OAT score in this case is above the 98th percentile, it is highly probable that this individual may be able to closely identify with individuals in recovery from substance use disorder, such as those found at recovery support groups, and therefore may be more willing to trust these recovering individuals and follow their recovery advice.
The client’s highly elevated SAT score (the highest score on this profile), which is higher on the graph than the OAT score, suggests that despite the client’s capacity to acknowledge the more obvious problems and negative consequences associated with his use of drugs, there are subtle aspects of his behavior, personality, and addiction that are extremely hard for him to acknowledge. In other words, he may not be able recognize the pervasiveness of his addiction, how it negatively affects and rules every aspect of his life with deeply held negative thinking patterns, beliefs and negative coping patterns driving his addictive behaviors.
Clients with a pattern of scores like this client who tend to be able to acknowledge heavy usage, negative consequences and problem behaviors, may still be convinced, sincerely deluded into thinking that they are not truly addicted. They will often present as more “superficial” saying things like “well, I go to work every day and do my job so I couldn’t be addicted”. Clients with elevated SAT scores (especially higher on the graph than their OAT score) tend to be more initially resistant to the need for treatment and are more likely to relapse. These clients tend to be detached from their feelings and have relatively little insight into the basis and causes of their problems (namely substance addiction). These clients typically need a more intensive level of treatment where they can receive constant support for their recovery efforts and can get the kind of group processing therapy needed to help them connect with their feelings and learn how to cope with them without drugs.
In providing treatment to this type of client it is important to recognize that underneath the many excuses (other than substance addiction) for their problems, there is an individual with a substance use disorder who is likely in pain and scared. Individuals with high SAT scores may not be in touch with the pain and fear, largely because they immediately numb any negative feelings with substances as soon as they appear, but the pain and fear. In this case, intensive treatment and group work has to be accompanied by sensitive and skillful clinical intervention that lets the individual know that somebody is aware of their fear deep within and that it will be a relief to let it out to begin healing.
We hope you find this useful information regarding clinical issues. As always, the Clinical Helpline at 888-297-2774 is open to serve you Monday through Friday, 9 am to 5 pm (EST).
PDF Version Available for Download
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
