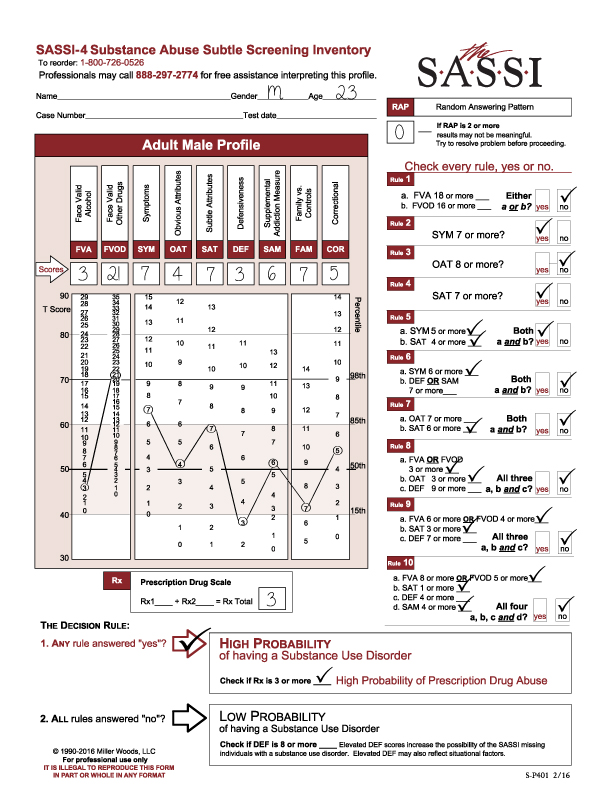
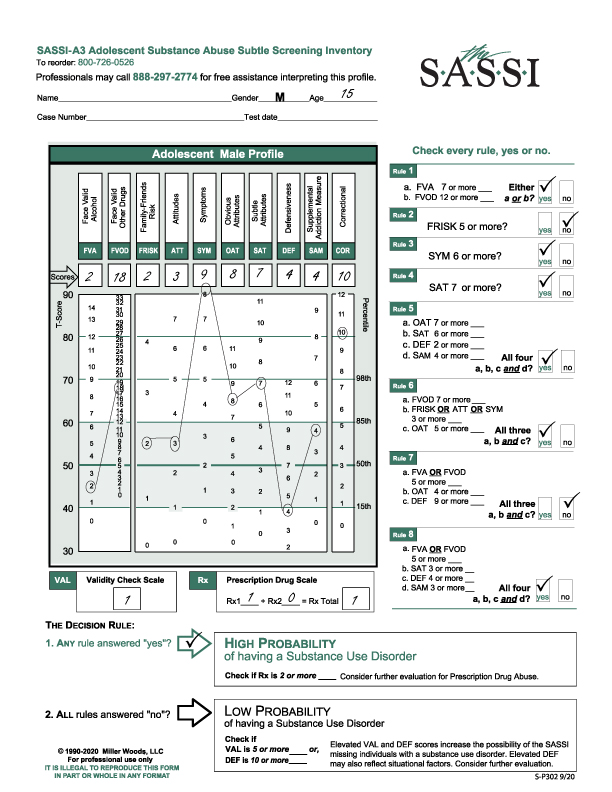
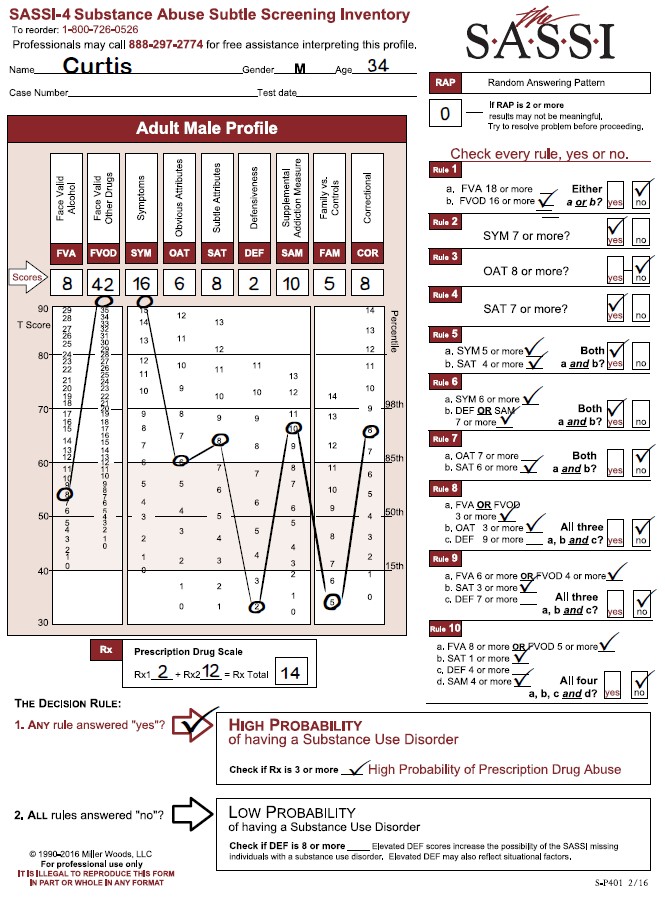
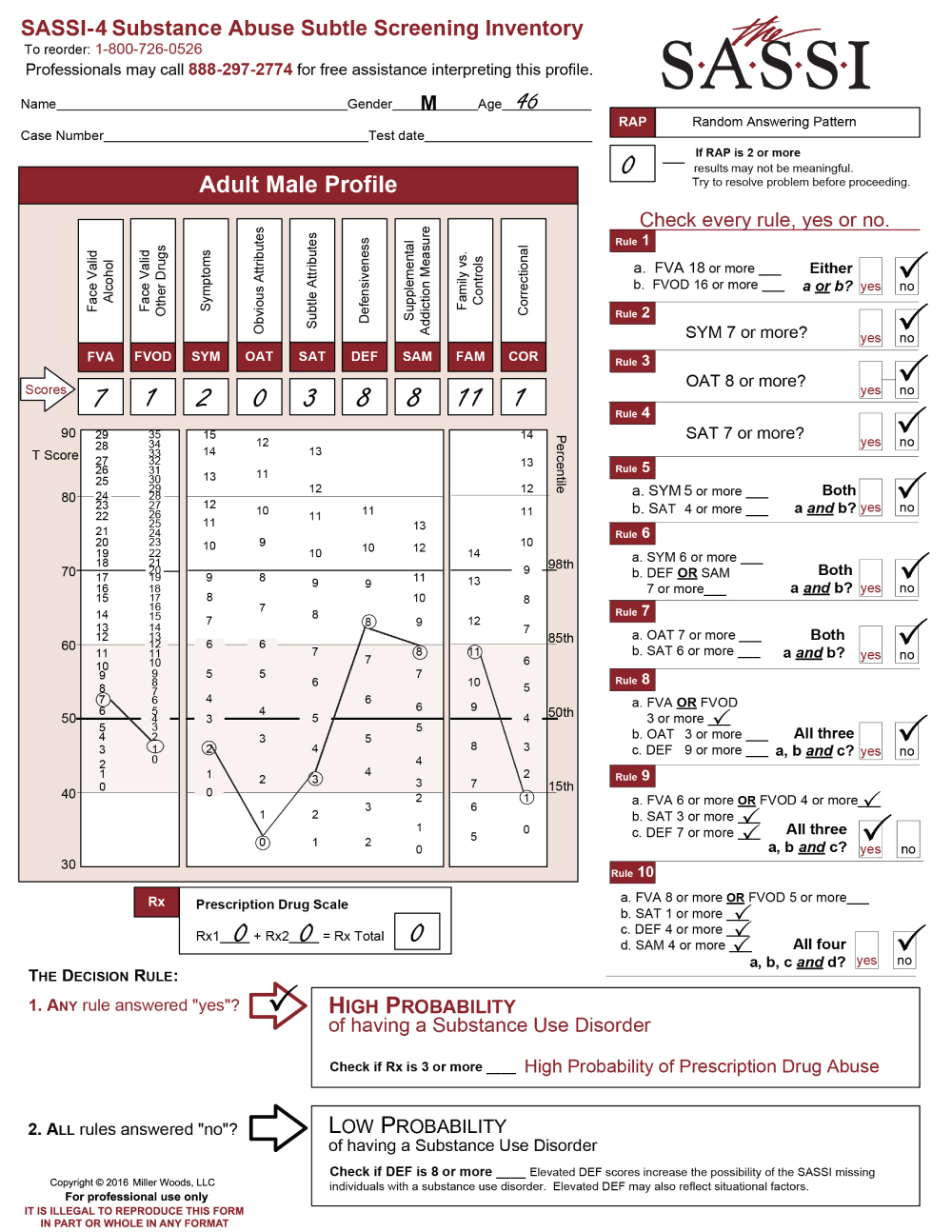
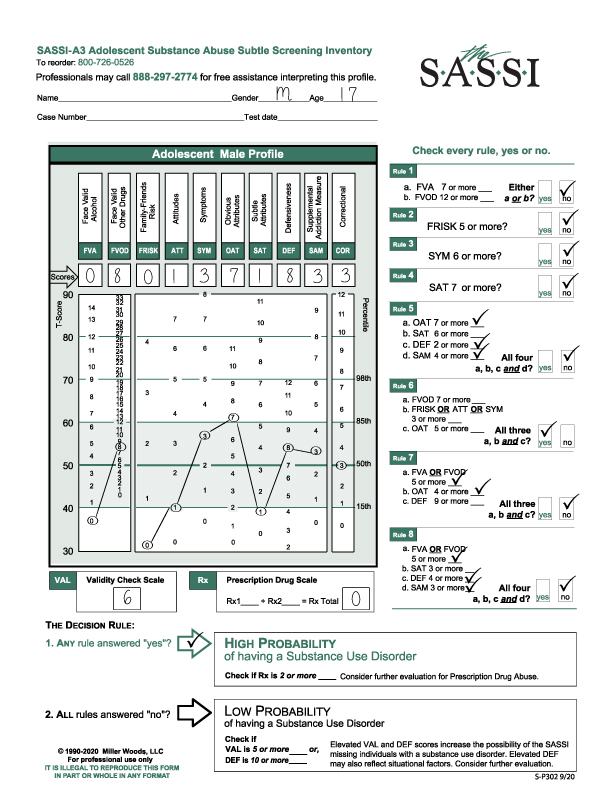
This adolescent male profile presents some initial complications for the reviewer in regards to the clinical interpretation as seen on the graph. The face valid scales fall either within the norm or below the norm. One of the subtle scales is above the 85th percentile so is clinically significant, and another is below the norm. An examination of the scales produces useful information to guide the discussion of the results with the client and directing appropriate treatment considerations.
This 17-year-old male completed the FVA/FVOD side of the questionnaire for his whole lifetime.
The VAL is 6.
Rx Scale is 0.
High Probability of a Substance Use Disorder is based on Rule 6.
Rule 6: a. FVOD 7 or more. (8)
b. FRISK or ATT or SYM is 3 or more. (SYM – 3).
c. OAT 5 or more (7).
Clinical Discussion
The FVOD of 8 is above average and should be noted. Examining those particular questions, he endorsed will provide the groundwork for how and under what circumstance he is using drugs. With the FRISK (0) and ATT (1) scores so low, his use is not necessarily tied to his peers, nor does he have a belief or value system that supports the idea that everyone uses substances. Looking at his one ATT score will help to evaluate any beliefs he may hold around substances.
The SYM (3) score is above average and again, because it is a face valid scale, content analysis will provide information regarding the consequences that he does acknowledge.
The OAT (7) scale is significant because it is elevated above the 85th percentile. This is the subtle scale that you want elevated as it indicates someone who can acknowledge limitations and shortcomings. He can probably identify with other substance users and those behaviors represented in that population such as impatience, resentment, self-pity, or impulsiveness. This, of course, does not mean he wants to or believes that he can change. But this information can be used as a positive to recognize the insights he may have around his use.
The low SAT (1) score (below the 15th percentile) gives some clues on how best to approach this client. This score indicates he is very hypersensitive to what others think about him. He may come across as having a chip on his shoulder so tread lightly!
The DEF (8) score, though above average, is still within the norm so does not indicate significant defensiveness on the client’s part.
The SAM (3) and COR (3) have no clinical significance.
Does the VAL score of 6 impact the results? Given the outcome was High Probability based on Rule 6, the impact is nil. The VAL is significant only if the outcome was Low Probability. However, with that score, the evaluator may hypothesize that perhaps the client was trying to skew the results but failed.
Questions remain regarding the current use of substances by the client. Is he minimizing his use or is he presenting an accurate picture? He was not defensive so perhaps his overriding concern was how he was viewed by the evaluator.
Treatment Considerations
Recommendations for the level of treatment need to be considered if he does have a diagnosable disorder based on the DSM-5. Actual current use also needs to be established. The elevated OAT score does indicate he will not feel out of place in a group setting. Prior history of substance use issues also need to be considered. It would appear, however, that outpatient treatment would be a consideration with the level of intervention to be determined by the overall assessment.
We recommend administrators of the SASSI have access to The Adolescent SASSI-A3 User Guide and Manual. It contains information on scoring, interpreting profiles and includes examples of profiles. It defines all the scales, what they represent, clinical considerations and giving feedback. The Manual also contains the research and validation information. Please call our Customer Service number for more information on how to order – 800-726-0526.