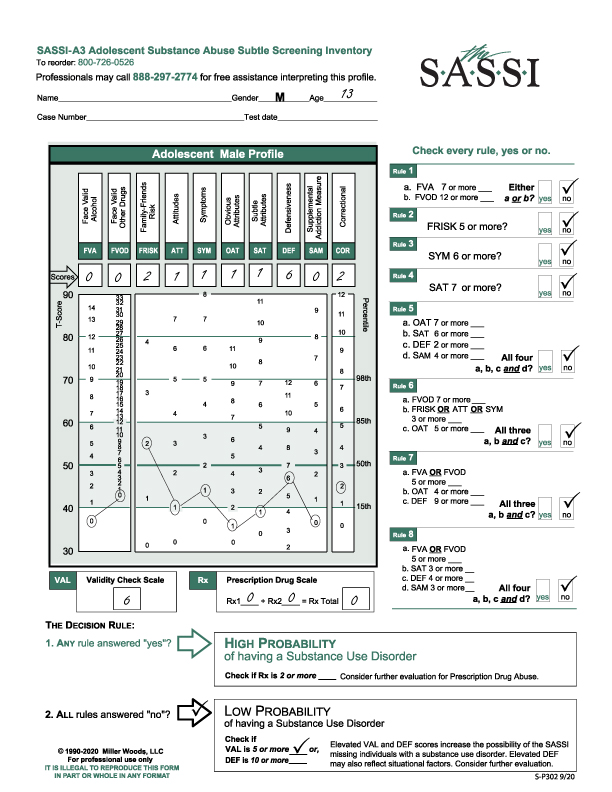
This is an issue that may be turning up in your clinical practice. The caller wanted help with a profile interpretation on a 13-year-old male who had turned in a vaping pen. The school was mandated to do a substance use evaluation as a result. The online report indicated “inconsistencies” in the results so the counselor wanted more information. The client was instructed to complete the FVA/FVOD side for his whole lifetime.
The overall result, based on all the rules being ‘no’, came up with a Low Probability of a substance use disorder. The Prescription Drug Scale was zero. However, the Validity Check Scale was 6 so further evaluation was recommended. Elevated VAL and DEF scores coupled with a Low Probability result increases the possibility of the SASSI missing individuals with a substance use disorder.
Looking at the graph on the profile sheet helps to pull out additional information. Note the very low (below the 15th percentile) OAT and SAT scores. The low OAT can indicate someone who has a hard time acknowledging personal limitations or shortcomings. The low SAT can indicate someone who has a chip on their shoulder, feelings of rejection and hypersensitivity to others. Interestingly, the DEF score is within the norm and does not indicate the student was defensive completing the SASSI. The FRISK score is above average but within the norm and because it is a Face-valid scale, content analysis of those items may be useful. The other Face-valid scales, ATT and SYM with their scores of 1 can also be examined.
The student who turned in the vaping pen indicated it was not his. It was not clear from the caller what substances they suspected were being used. Clinically, the best thing to keep in mind is that the student has a hard time opening up and is probably very concerned about how he is viewed by teachers, counselors, etc. and very quick to feel rejected. Interacting with him in an accepting and affirming way is probably the best approach.
Substance use issues: The VAL of 6 is a red flag so further evaluation with this student is warranted. It could be on-going oversight within the school, i.e. school counselor or referral to a Substance Use counselor who could do a more formal and comprehensive assessment.
We hope this is useful for you.
As usual, don’t hesitate to call the Clinical Helpline at 800-726-0626 with any clinical questions. Live clinicians are available M-F, 11-5 pm (EST). Otherwise, feel free to leave a message and we will get back to you the next business day.