It is no news that the use of marijuana is viewed by many, no matter what the demographic, as innocuous and far less than alcohol and certainly any other drugs. It has become increasingly difficult to convince users of the harm associated with marijuana use when the legal status ranges from fully illegal, to medicinal and/or decriminalized to fully legal. Users often describe marijuana as simply a plant so it is a natural and therefore a healthy alternative to alcohol and other drugs. This, along with the misconception that marijuana is not addictive, creates an inherent struggle for both the evaluator and evaluatee. As an aside, when writing this, I came across an article in the New York Times by Dana G. Smith (April 10, 2023), titled “How Do You Know If You Are Addicted to Weed?” The article itself gives good basic information but the most interesting part was the comments from readers which were all over the map.
Substance use evaluations for marijuana use become problematic when the client comes in with that strong point of view which may be reflected in the results of the SASSI and in the scales.
The question of diagnosis based on the DSM-5’s 11- symptom criteria and whether the client meets either mild, moderate or severe must be answered before any treatment considerations can be raised.
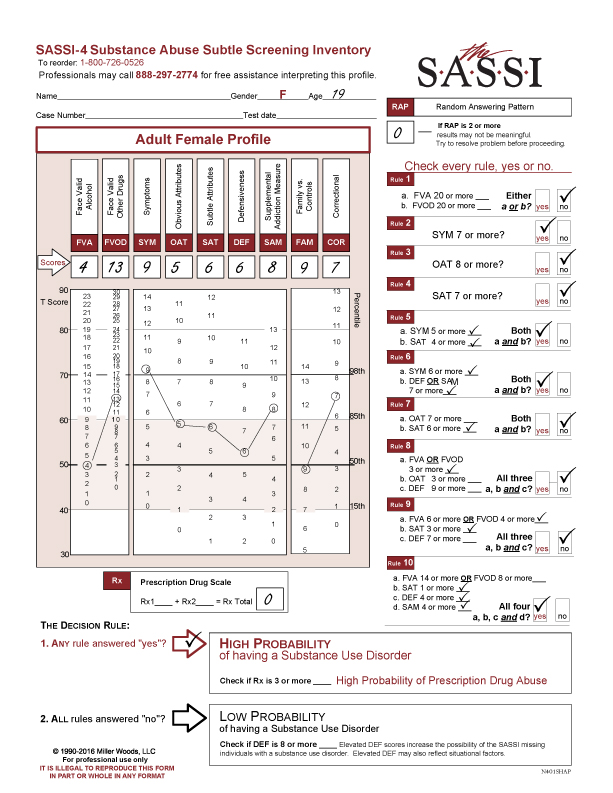
The following is a good example of what a profile looks like when the drug use in question is marijuana.
The client is a 19 year old female and the FVA/FVOD questions were answered for the last 12 months. The RAP and Prescription Drug Scale scores are 0.
CLINICAL INTERPRETATION
The client’s FVA is average but her FVOD of 13 is elevated above the 85th percentile so clinically significant. Her SYM score of 9 is above the 98th percentile so she is endorsing significant symptoms and consequences. It also indicates she is associating with either family or friends who are heavy users. This gives important information regarding her environment and the difficulty of a social system that supports recovery.
The OAT scale score of 5 is neither elevated nor extremely low. It would be plausible to say she does not identify with or see herself as a substance abuser. This is reinforced by both the SAT(6) and DEF(6) falling in the normative range. She is not in denial because she believes there is nothing wrong with smoking marijuana and so was non-defensive when completing the questionnaire. The only other clinically significant scale is COR with a score of 7, also above the 85th percentile. Whether or not she has legal problems, she has answered in a similar way to others with legal issues. Anyone looking at that result can evaluate impulsivity, anger management issues, low frustration tolerance, poor social skills or risk taking behaviors, all of which impacts choice-making abilities.
THE RULES
Out of the 10 rules evaluating for either a high or low probability of a substance use disorder, she meets 4 of them:
Rule 2 (SYM=7+)
Rule 5 (SYM=5 + and SAT=4+)
Rule 6 (SYM=6+ and DEF OR SAM=7+)
Rule 10 (FVA=14+ or FVOD =8+ and SAT=1+ and DEF= 4+ and SAM 4+)
To meet the criteria of a High Probability of a Substance Use disorder requires meeting only ONE rule. Meeting more than one rule does not necessarily mean a more severe disorder. The DSM-5 evaluates for severity ranging from mild, moderate to severe based on the number of diagnosable criteria met.
CLINICAL ISSUES TO CONSIDER
Giving clinical feedback to this client or any client for that matter, is to use the information they have given you from the questionnaire. Pulling information from this client’s questionnaire, the FVOD and the SYM responses can help start the conversation regarding how she is using drugs, under what circumstances and consequences of her use. For online users wanting access to the SYM questions, go to sassionline.com, log-in: go to ‘my clients’ tab; then ‘support materials’ tab. Under Adult SASSI-4 Online User’s Guide go to the SYM section, Pg.19. You will find a list of the SYM questions you can coordinate with your client’s completed questionnaire. A reminder: only with face valid scales i.e FVA, FVOD, SYM and Rx scales can you do content analysis of the questions.
The purpose of feedback is not trying to convince her that marijuana is a drug and she has a disorder but to use the information she, herself, has given you to explore how her drug use is impacting her in a negative way or in some ways interfering in her life.
TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS
The OAT score result implies group treatment intervention would not be the first choice for this client. Information specifically regarding marijuana’s addictive qualities and impact on the body could be included in individual motivational counseling. Establishing a goal regarding her use, including reduction or abstinence is part of treatment planning no matter the context. Even though she is not defensive, establishing rapport and trust may be instrumental in facilitating this client to take a closer look at her drug use and eventually be open to group experiences.
If you have any clinical questions, be sure to call our free helpline to talk to our clinicians. We are available M-F, 12-5 EST at 800-726-0526.
PDF Version Available for Download