Many people know that the SASSI is possibly the best substance use disorder screening tool that exists in the behavioral health field today. The instrument can be easily administered in 15 minutes or less and manually scored in less than two minutes (or scored automatically in the online web-based version), resulting in an objective empirically-based statement of the likelihood of the client having a substance use disorder with an overall accuracy of 92% for adults and 89% for adolescents. And it achieves this kind of accuracy even in clients who are unwilling or unable to acknowledge their substance misuse or the symptoms associated with it!
Through extensive case study research, the SASSI has been found to be able to provide even more utility to clinicians in the form of clinical interpretations that go beyond just the high or low probability of a substance use disorder result. In addition to interpretations of individual scale raw scores that fall outside the boundaries of the research-based established normal distribution, we also have discovered some trends or characteristics in the specific situation in which the client scores as high probability of a substance use disorder based on SASSI decision rules that involve only subtle scales rather than face valid scales. That is the subject of our blog today.
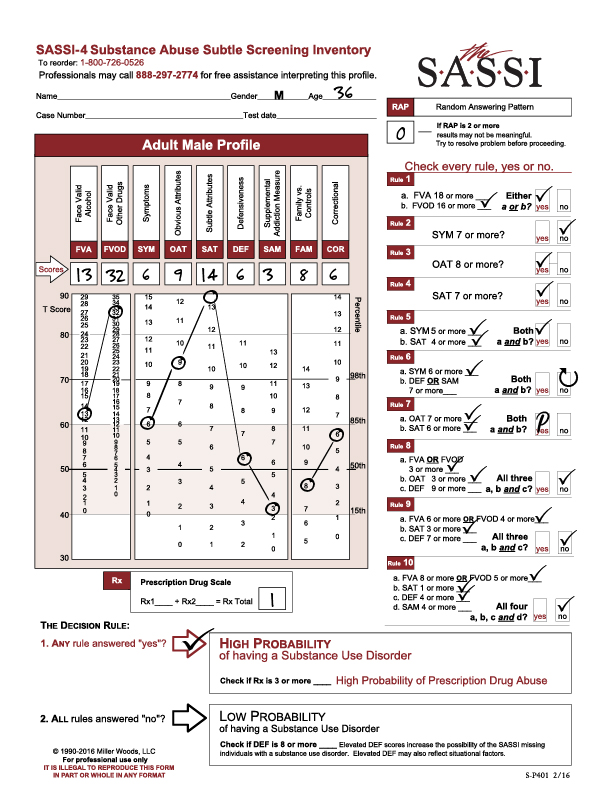
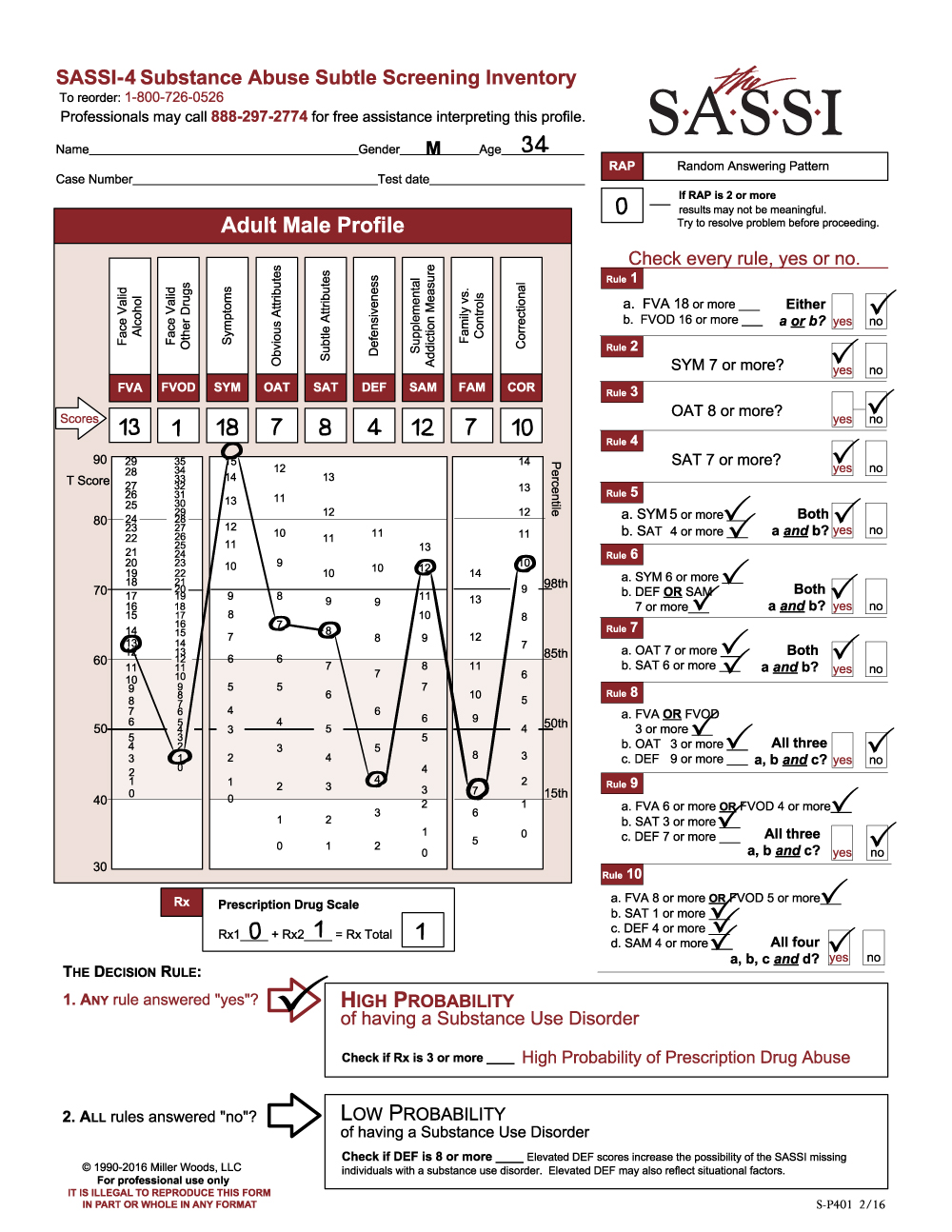
The SASSI is made up of both face-valid scales and subtle scales. Face-valid scales such as FVA, FVOD and SYM are scales that are very obvious about what they are measuring, while subtle scales such as OAT, SAT and DEF are made up of items that do not seem to have anything at all to do with substance use. Our case study analysis showed that certain behaviors, characteristics or patterns emerge in individuals who score as high probability based only on subtle scales. Let’s take a look at an example. Byron is a 31-year-old male who was asked to be evaluated because of a child custody battle in which the mother alleges that Byron misuses drugs. Byron has not yet had a comprehensive assessment done, but has so far only admitted to some occasional use of marijuana. A SASSI was administered and the results showed that Byron met the criteria for Decision Rules 3, 4 and 7. Each of these decision rules involve only subtle scales and no face-valid scales. So, what characteristics do we tend to find in individuals with this type of scoring pattern?
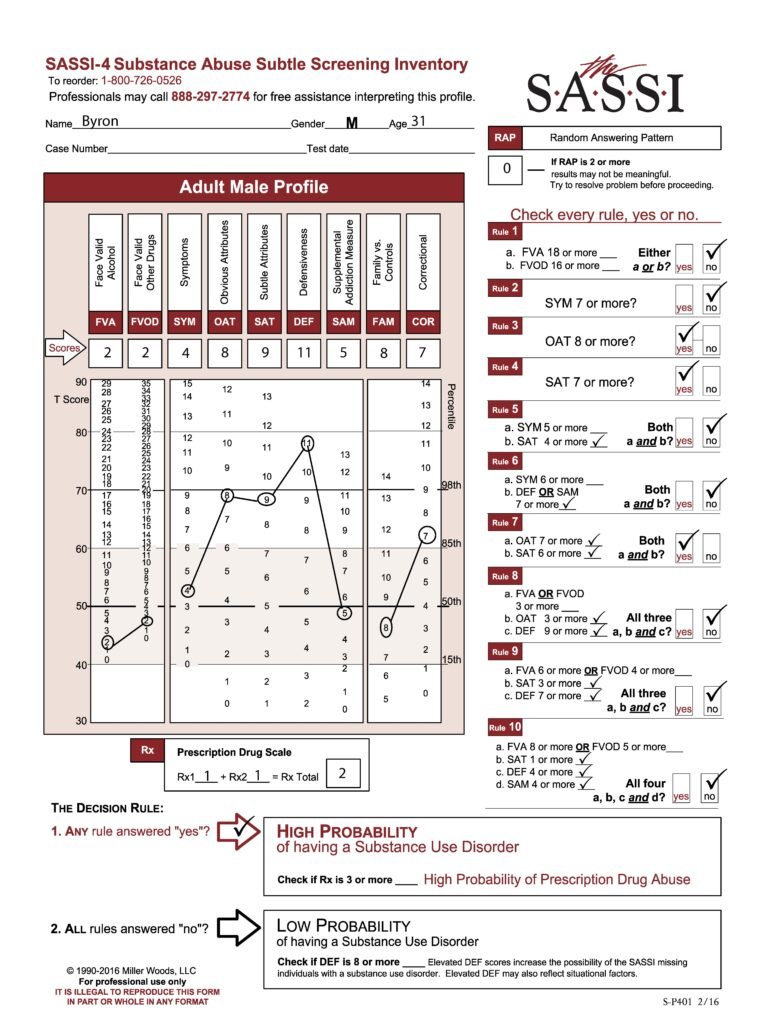
One key feature of this type of scoring pattern is the fact that these individuals often have very little insight into the pervasive nature of the addictive disorder in their lives. Most of the time, this type of client actually has a very sincere delusion regarding their substance misuse. In other words, they are not trying to trick you into thinking they do not have a problem with substances; they simply do not see it. Often, every single activity this person is engaged in and every decision they make somehow involves substance use. Often, the substance misuse has become an unhealthy way to cope with emotions that are too overwhelming and so individuals with this type of scoring pattern are very emotionally avoidant. Many times, this individual has difficulty admitting their weaknesses or the personal limitations with which they struggle and instead choose to focus on very superficial things, ignoring the depth of the substance problem in their life. We can see these types of traits and behavior patterns manifested in this client’s individual face-valid scale scores such as lower than average (T-score of 50 is the mean) FVA and FVOD scores and only an average SYM score. These all indicate a client who does not acknowledge or admit to having any significant problems or negative consequences as a result of substance use. The client’s extremely high DEF score indicates a very high level of guardedness and the desire to be seen as having no weaknesses or faults. It’s even possible that the FVA, FVOD and/or SYM scale scores could be artificially low because of minimization of symptoms in the client’s answering patterns on these scales fueled by this defensiveness. However, as mentioned previously, it’s possible and even probable that this client really has very little insight into his problem with substance misuse and so he may be unable to even recognize the obvious negative consequences he is experiencing. This is especially typical of clients with high SAT scale scores as this client has. While this client does also have an equally high OAT score, which often indicates some ability to recognize negative attributes that are common in individuals with substance problems such as impulsiveness, self-pity, resentment, and impatience, it is more likely in this case that the client does not see these issues as having any relationship to his misuse of substances.
At this point, a comprehensive assessment needs to be done along with a formal diagnosis and possible treatment plan formulated. Since the SASSI does not provide an actual diagnosis and does not, by itself, indicate a need for treatment or the level of treatment, it is important to gather more information such as self-reports of the client’s current usage patterns, collateral reports, naturally occurring records, behavioral records, etc. to determine a diagnosis and course of action. Typically, clients with this scoring pattern do have a significant substance use disorder and many of them, if they need treatment, will often need a relatively intensive level of treatment which includes individual and group therapy sessions; more than just cognitive/educational programming. However, individuals with this type of scoring pattern will often be initially resistant to any treatment as they honestly do not see a problem that needs to be treated. The high level of defensiveness will require lots of time spent in developing a therapeutic alliance and positive rapport, affirming and supporting him throughout the process. Clients like this are often a high relapse risk and so it is important to provide wraparound supports and a level of intensity in the treatment regimen which allows for quicker and stronger intervention in the event the client attempts to relapse. Individuals who score as high probability of a SUD based only on subtle scales are often some of the most challenging clients, but with information gained from the client’s scoring patterns on the SASSI combined with additional information from other sources, you are in a better position to know what to address to increase the possibility of success with this client.
Don’t forget that full training on administering/scoring the SASSI and clinical interpretation of the sub-scales is available. Check out https://sassi.com/sassi-training/ to register for an upcoming training. Also, our free Clinical Helpline is available M-F from 1:00pm to 5:00pm EST to answer any questions you have about the SASSI.