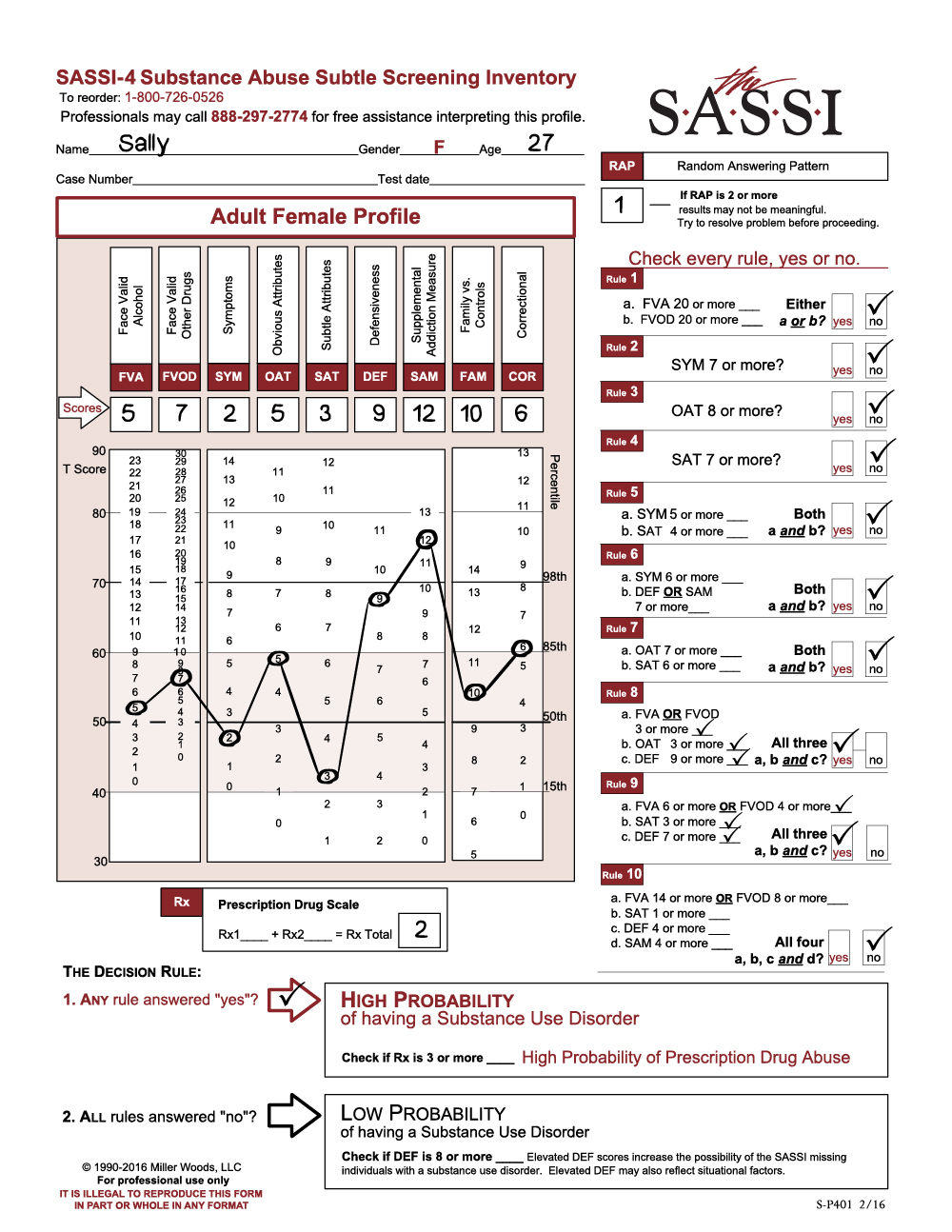
We frequently receive calls requesting clinical interpretation of profiles done on Department of Transportation (DOT) clients. These clients have failed their drug/alcohol screening and their license to drive has been suspended pending an evaluation. In this particular case, the client is a 68-year-old female whose alcohol level registered above the DOT threshold. Her SASSI result indicated a high probability of a substance use disorder based on Rule 9. As you see on the graph, most of the scale’s clinical results fall within the norm. DEF, at 11, is above the 98th percentile and FAM, at 12 is above the 85th percentile. The OAT score of 1 falls in the 15th percentile. The high-DEF score is not unusual in DOT evaluations. It is incumbent on the evaluator to determine what the defensiveness is about. The SAM scale is no help in this case because it is not elevated. An elevated DEF coupled with an elevated SAM indicates the defensiveness is related to substance use. The elevated FAM score indicates someone who is not comfortable looking at their own issues. And the low OAT score indicates someone who has difficulty acknowledging their personal limitations and shortcomings. The combination of these three scales provides information to the evaluator that most likely, this client is not going to be forthcoming in disclosing issues or problems. During the evaluation, another piece of information disclosed was the client’s admission of trying to manage or monitor her drinking to try to stay below DOT’s threshold of alcohol use. That certainly may be a red flag.
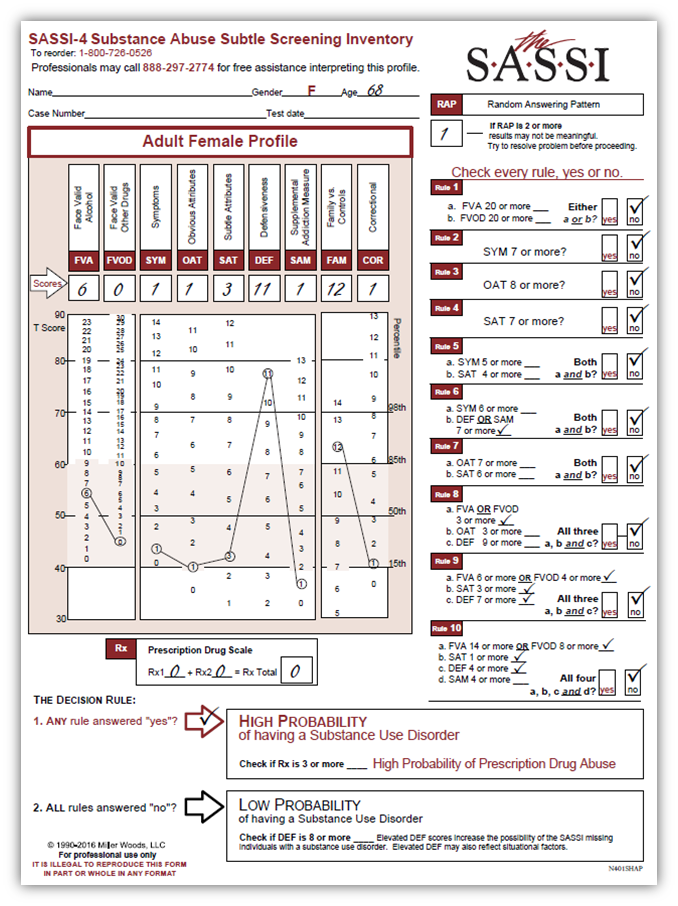
Since the SASSI is a screening inventory and does not diagnose, the evaluator needs to reference the DSM-5 to determine if, indeed, the client meets the criteria for a substance use disorder and if so, what level – mild, moderate, or severe. Based on that, the evaluator has a couple of options to consider. If possible, work individually or refer to an individual substance abuse counselor to establish rapport and work to get the defensiveness down. Motivational Interviewing is a good asset to pull out in this case. Another option is to refer her to an outpatient group setting with the goal of connecting her to other clients and also have access to individual counseling as well. Regardless, outpatient treatment seems to be the most likely intervention.
It would be helpful to acknowledge the financial impact on the client that suspension of driving privileges is having on her. That certainly could be triggering the extreme defensiveness we see in the results and the consequences for the client could be significant.
We hope these reviews are helpful and whether you are a new user or a very experienced one,
clinicians are here to help with any questions you might have. Clinicians are available M-F, 11-5 (EST). Call us at 800-726-0526 or 888-297-2774.